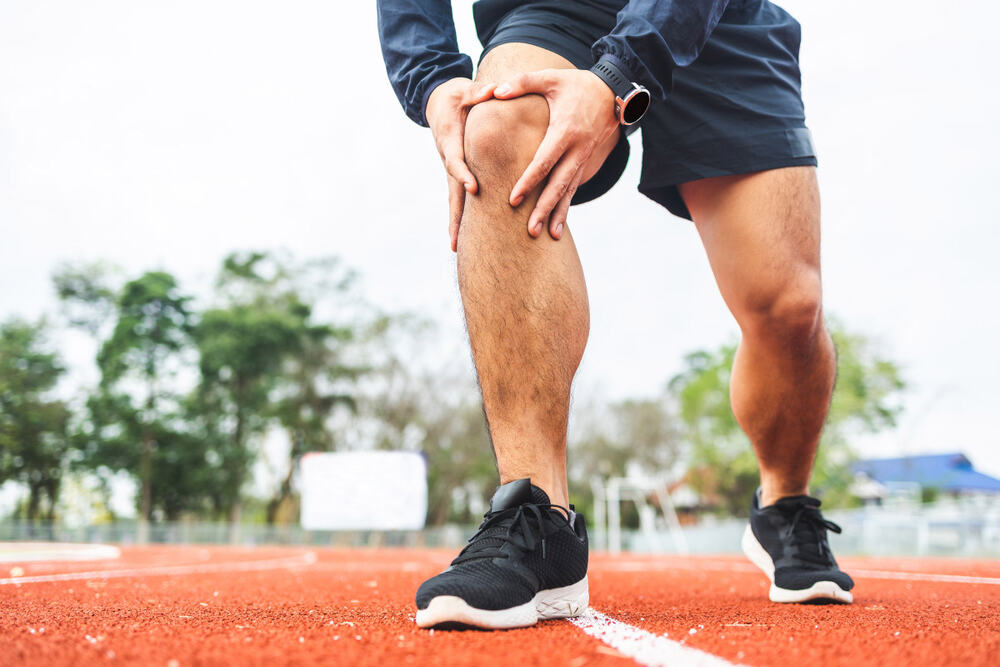
An ACL injury, a tear or sprain of the anterior cruciate ligament in the knee, often affects athletes. It typically occurs during sudden stops, jumps, or directional changes. The injury can cause swelling, pain, and instability. Timely diagnosis and treatment, including rehabilitation or surgery, are crucial for restoring knee function.
What are the symptoms?
- A sudden loud pop or popping sound inside the knee
- Sharp pain, preventing further activity
- Rapid swelling
- Limited range of motion
- Feeling that the knee may “give out” under weight
Why does this disease occur?
ACL injuries happen when the ligament connecting the thigh and shin bones stretches or tears. Common causes include abrupt changes in direction, pivoting with a planted foot, awkward landings, sudden stops, and direct impacts during contact sports. Mild injuries may only stretch the ligament without a complete tear.
Who is at risk of this disease?
- Female athletes, due to anatomical and hormonal differences
- Players in soccer, basketball, football, gymnastics, or downhill skiing
- People with weak conditioning or incorrect movement patterns
- Users of poorly fitting footwear or damaged sports equipment
- Individuals playing on artificial turf
How is this disease diagnosed?
Physical exam: Checks swelling, tenderness, and motion range
X-rays: Rule out fractures
MRI: Reveals ligament, cartilage, and soft tissue damage
Ultrasound: Evaluates ligaments, tendons, and muscles
What are the possible complications?
- Higher risk of knee osteoarthritis, even after surgery
- Persistent instability or repeated injuries
- Long-term mobility issues, if untreated or poorly rehabilitated
What is the treatment?
- Immediate care: R.I.C.E (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation)
- Rehabilitation: Strengthening and stability exercises with a physical therapist
- Surgery: ACL reconstruction using a tendon graft, followed by intensive rehab for athletes or severe tears
How can you take care at home?
- Rest and limit weight-bearing activities
- Ice the knee regularly
- Use compression wraps
- Elevate the knee
Follow prescribed exercises to regain strength and mobility
How can this disease be prevented?
- Strengthen core, hip, and leg muscles
- Practice proper jumping, landing, pivoting, and cutting techniques
- Wear appropriate footwear and protective gear
- Ensure sports equipment is correctly maintained
- Avoid inward knee movement during exercises
When should you see a doctor?
- After a loud pop or a painful knee injury
- If swelling or instability persists
- If the knee “gives out” during daily activities
- If previous knee injuries worsen
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Can ACL injuries heal without surgery?
Mild ACL injuries may recover with rest, rehabilitation, and strengthening exercises. Severe tears often require surgery.
Q2: How long before an athlete can return to sports?
Recovery can take 6–12 months. Full rehabilitation and stability assessment are essential before resuming high-risk activities.
Important Note: This information is for awareness only. Please consult a healthcare professional for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.